How Much Does Your State Collect in Corporate Income Taxes per Capita?
by Janelle Cammenga, Tax Foundation, March 4, 2020
This week’s map compares corporate income tax collections per capita among the 50 states. The states with the highest collections are New Hampshire ($582), Massachusetts ($349), California ($315), Alaska ($266), and Delaware ($263). States with the lowest corporate income collections per capita are South Dakota ($37), New Mexico ($44), Arizona ($52), Missouri ($54), and Oklahoma ($60).
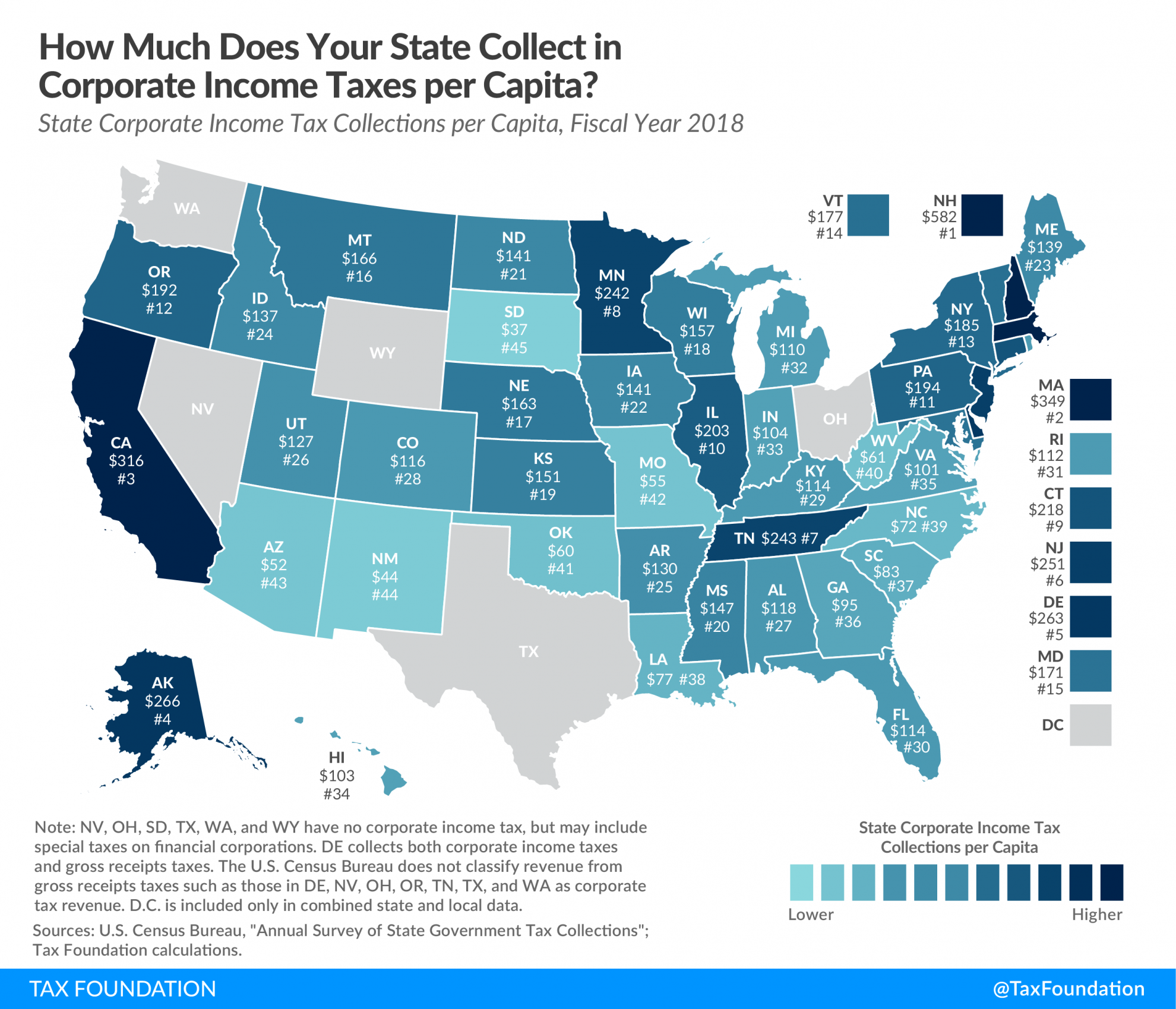
Six states—Nevada, Ohio, South Dakota, Texas, Washington, and Wyoming—do not levy a corporate income tax. However, in some states without a corporate income tax, a small amount of corporate income tax revenue is shown (such as in Ohio and South Dakota) due to taxes on specific types of businesses (such as financial institutions), which are sometimes structured as corporations.
It is important to note that among the six states without a corporate income tax, four (Nevada, Ohio, Texas, and Washington) instead have state-levied gross receipts taxes on businesses. The U.S. Census Bureau does not classify revenue from gross receipts taxes as corporate income tax revenue, but gross receipts taxes are generally considered more economically harmful than corporate income taxes due to tax pyramiding, non-neutrality, and lack of transparency. Delaware, among the states with the highest corporate income tax collections per capita, has both a corporate income tax and a state-levied gross receipts tax.
When thinking about business taxes, the corporate income tax may be among the first that comes to mind, but it is far from the only tax businesses pay. In addition to corporate income taxes, corporations are subject to sales, property, unemployment insurance, excise, payroll, and business license taxes, among others. In fiscal year 2018, corporate income taxes accounted for only 8.5 percent of all taxes paid by businesses to state governments.
Compared to other sources of tax revenue—such as income, sales, and property taxes—states rely relatively little on corporate income taxes. According to the U.S. Census Bureau, in fiscal year 2017, the corporate income tax generated only 3.2 percent of total state tax collections.